Column Finance and the Social Security System 2020.08.25
【Aging, safety net and fiscal crisis in Japan】No.266: Alcoholism
In this column series, Yukihiro Matsuyama, Research Director at CIGS introduces the latest information about aging, safety net and fiscal crisis in Japan with data of international comparison.
According to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)’s Health Statistics in 2020, the annual alcohol consumption per capita is 7.2 liters in Japan, which is relatively low compared to other developed countries (Figure 1). However, the number of outpatients that sought psychiatric care to treat alcoholism increased from 92,054 in 2014 to 102,148 in 2017 (Figure 2). Among them, the number of patients who received inpatient treatment increased from 25,548 to 27,802 in the same period. Figure 3 shows the distribution of the 9,250 patients that visited a medical institution specialized in alcoholism in the 2018 Fiscal Year by gender and age group. This reveals that 50% of the patients were between 40 and 59 years old (in other words, they were part of the working generation).
The government considers a daily intake of 40g or more of pure alcohol for males, and 20g or more for females, the threshold for increasing the risk of lifestyle-related diseases. Figure 4 shows the percentage of people who consume alcohol exceeding this standard by gender. While the percentage for males has not declined, the percentage for females has risen. As such, the government aims to reduce it to 13.0% for males and 6.4% for females by 2023.
Figure 1: Alcohol consumption per capita per year
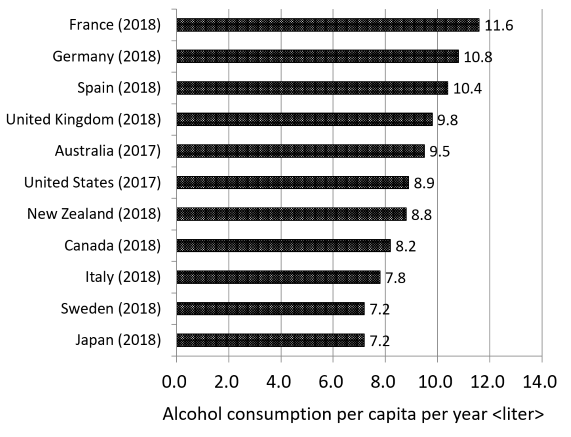
Source: OECD Health Statistics, 2020
Figure 2: Number of alcoholics who sought psychiatric care
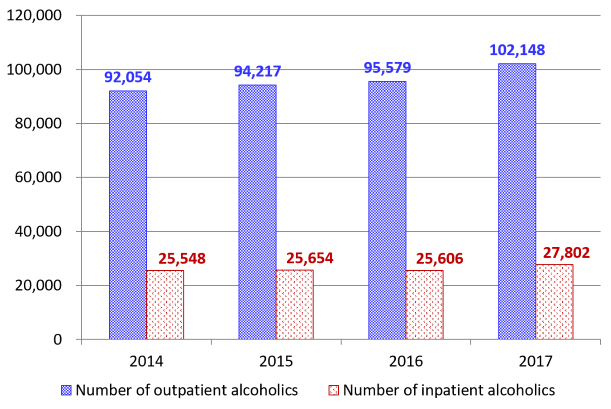
Source: Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare
Figure 3: Number of patients who visited a medical institution specialized in alcoholism in the 2018 fiscal year
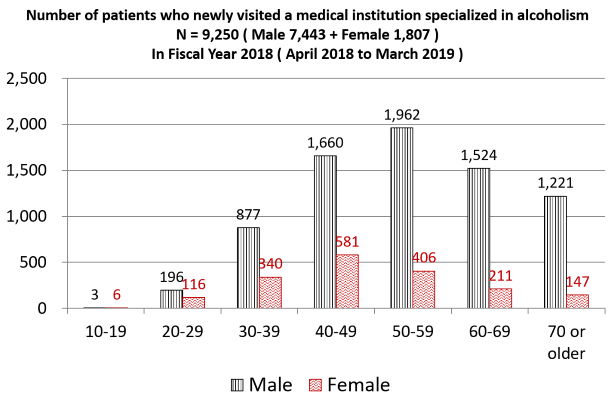
Source: Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare
Figure 4: Percentage of people (aged 20 or older) that drink alcohol that increases the risk of lifestyle-related diseases in the population (i.e., 40g or more for males and 20g or more for females).
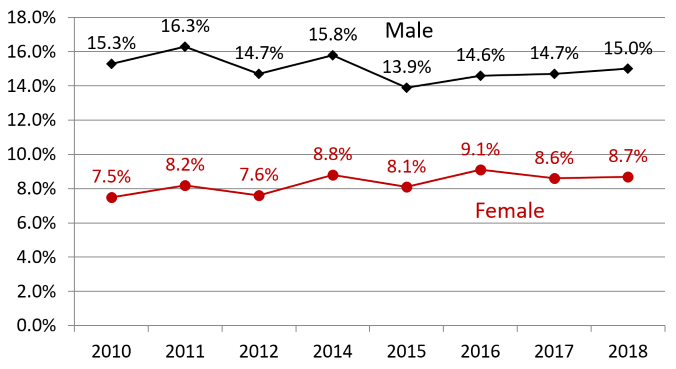
Source: Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare
