Column Finance and the Social Security System 2020.01.30
【Aging, safety net and fiscal crisis in Japan】No.215: Profit margin inequalities among private hospitals
As mentioned in Column No. 3, there is a problem of overinvestment in Japan's healthcare delivery system. For example, the United States, which has a population of 326 million, has 6,210 hospitals, whereas Japan, which has a population of 126 million, has 8,292 hospitals (Table 1). The number of psychiatric hospitals in Japan that have been internationally criticized for too long hospital stay of their patients is 1,054 as compared to 605 in the United States.
While there are more than 20 types of medical institutions that run hospitals, 5,714 hospitals out of 8,292 are organizations called "Medical Corporation". As shown in Column No. 197, most of them are privately owned for-profit entities. Medical corporations are classified into four types: those that run general hospitals, psychiatric hospitals, general clinics, and dental clinics. The Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare conducted a medical economics survey to observe the changes in the profit margin of medical corporations and create a reference for the revision of medical fees every two years. However, this survey was based on a questionnaire and the sample size was small. Further, the data showing the financial status of all the medical corporations in Japan have not yet been collected. Therefore, I collected the financial statements of 6,478 medical corporations from seven prefectures (Hokkaido, Kochi, Kyoto, Hyogo, Gunma, Tottori, and Nara). The data were then aggregated to identify the characteristics of the financial structure of medical corporations.
Figure 1 shows the distribution of profit margins of medical corporations that run general hospitals. Medical corporations with revenues exceeding JPY 10,000 million have stable business performances and small differences in profit margins. This is because comprehensive care is provided to patients by operating clinics, rehabilitation facilities, and nursing care facilities along with hospitals. However, there is a large difference in the profit margins, ranging from minus 30% to plus 20%, among medical corporations with revenues less than JPY 5,000 million. Many corporations in the red are medical institutions with a standalone small- or medium-sized hospital that cannot meet the needs of local residents. Figure 2 shows the distribution of profit margins of medical corporations that run psychiatric hospitals. Their average profit margin is 4.6%, with some exceeding 10% every year.
(For details on the profit margins of general clinics and dental clinics, please refer to Column No. 216)
Table 1 Number of hospitals in The United States and Japan
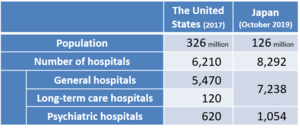
(Source) American Hospital Association (AHA) . Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare
Figure 1 Distribution of profit margins of medical corporations operating general hospitals
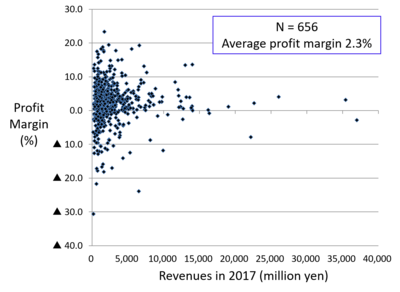
(Source) Financial statements of medical corporations provided by seven prefectures
Figure 2 Distribution of profit margins of medical corporations operating psychiatric hospitals
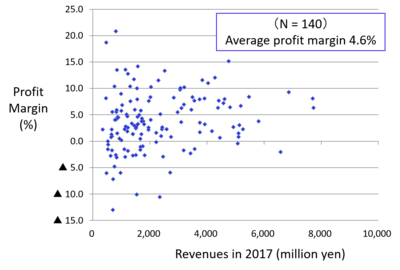
(Source) Financial statements of medical corporations provided by seven prefectures
