Column Finance and the Social Security System 2019.07.26
【Aging, safety net and fiscal crisis in Japan】No.205:Pharmacy dispensing medical expenses keep increasing
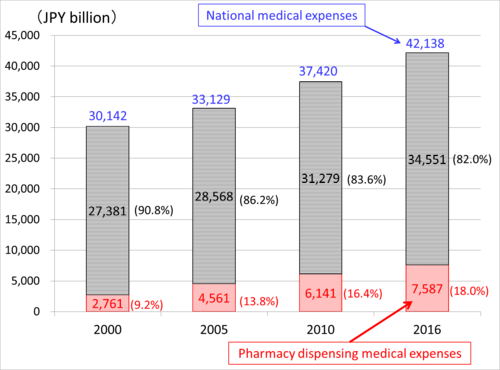
As Figure 1 shows, Japan's national medical expenses increased by 40% from JPY 30,142 billion in 2000 to JPY 42,138 billion in 2016. During the same period, pharmacy dispensing medical expenses increased by 275% from JPY 2,761 billion to JPY 7,587 billion. Consequently, the ratio of pharmacy dispensing medical expenses to national medical expenses rose from 9.2% to 18.0%.
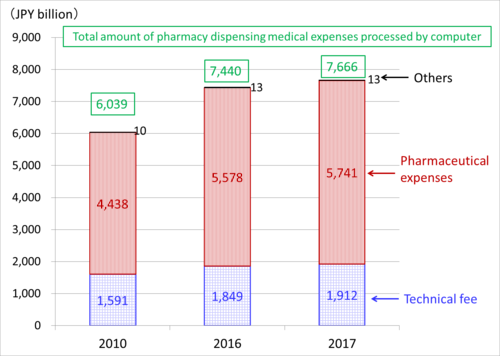
Pharmacy dispensing medical expenses are the costs to provide doctor-prescribed medications to a patient. The expenses break down into technical fees, pharmaceutical expenses, and others. The technical fee is the price paid to a pharmacy for the specialized ability to dispense prescription drugs and provide them to a patient, and to provide patient instruction. There are two types of pharmacies: those in medical institutions and those in organizations independent of the medical institution. The government decided to pay an additional technical fee to independent pharmacies outside medical institutions to facilitate the division of diagnosis and dispensing. Consequently, technical fees expanded from JPY 1,591 billion in 2010 to JPY 1,912 billion in 2017 (Figure 2). This is the background of the rapid increase in the number of pharmacies mentioned in Column No.150.
However, increasing the number of independent pharmacies did not solve issues such as the phenomenon of polypharmacy among elderly people effectively (see Column No. 125). Therefore, the government is planning to promote a regional formulary program. A regional formulary is a standardization scheme for prescription drugs in each region to improve the safety and efficiency of prescriptions. This means that technical fees, which are pharmacies' revenue source, is likely to decrease in the future.