Column Finance and the Social Security System 2018.03.27
【Aging, safety net and fiscal crisis in Japan】No.77: Decline in Labor Share Ratio
In March 2018, the Ministry of Finance released a report titled "Financial Statements of Corporations by Industry, Quarterly Oct. - Dec. 2017." The operating profit margin in the 4th quarter of 2017 is 5.8%, 7.4%, 5.2% for all industries, manufacturing industries, and nonmanufacturing industries, respectively, and corporate earnings continue to be strong. However, the decline in the labor share ratio is regarded as a problem.
Labor share ratio is the share of the total value added by companies that is attributable to workers. The Ministry of Finance calculates it by dividing total personnel expenses by the total value added. Total personnel expenses are the sum of salary / bonus and benefit welfare expenses, and the total value added value is defined as "personnel expenses + operating net profit + interest expense + tax + movable property / real estate rent."
As shown in Figure 1, the labor share ratio of medium enterprises (capital of JPY 100 million or more, but less than JPY 1 billion) and small companies (capital of JPY 10 million or more, but less than JPY 100 million) is stable at around 70%. However, the ratio of large companies has decreased to 55.9% - despite the increase in their revenues and profits - after it had reached an abnormal level of 101.6% in the first quarter of 2009, immediately after the shock caused by the Lehman bankruptcy. In other words, although there is a source available to raise wages, large companies are reluctant to utilize it.
Figure 2 shows the trends in the labor share ratio of developed countries during the period from 2010 to 2015. Japan's labor share ratio of 65.3% for all industries in the fourth quarter of 2017 is not much lower than that of other countries.
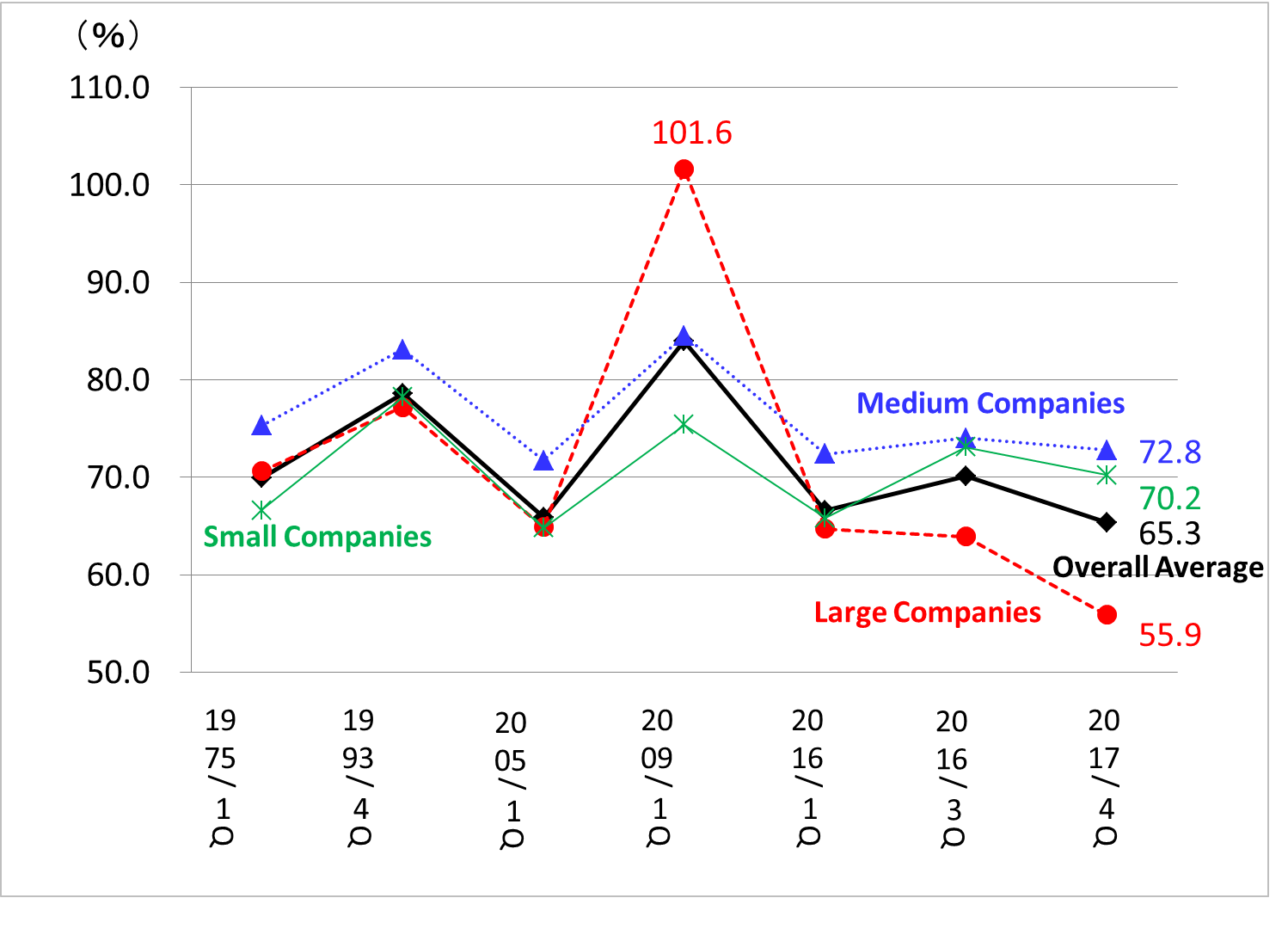
(Source)Ministry of Finance
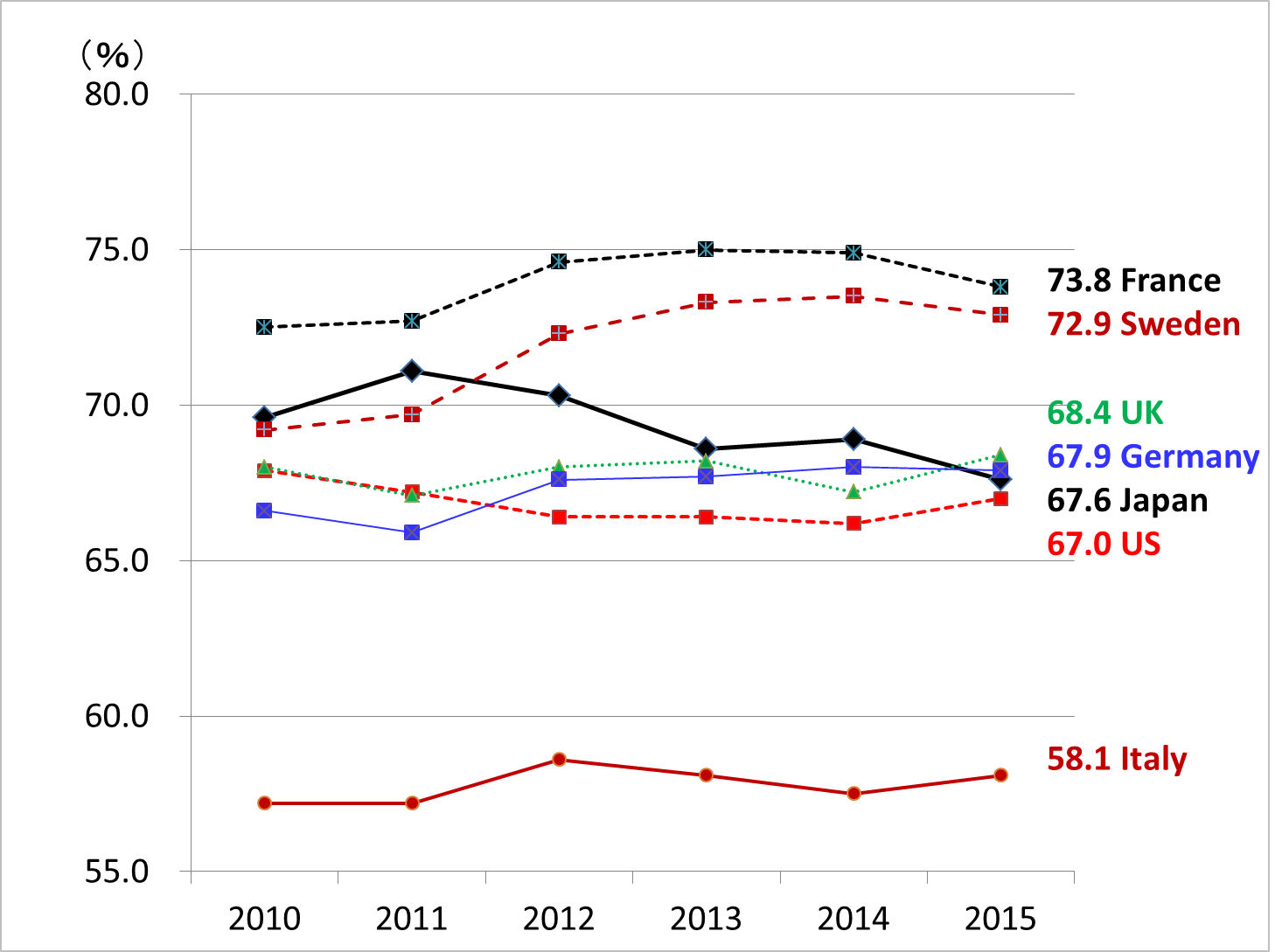
(Source)Japan Institute for Labor Policy and Training, 2017 Databook of International Labor Statistics
