Column Finance and the Social Security System 2018.01.24
【Aging, safety net and fiscal crisis in Japan】No.14: Healthcare IT Investment
As shown in Figure 1, according to the survey of the Japanese Association of Healthcare Information Systems Industry, the amount of IT investment in Japan's health care industry was 563 billion yen (US $5.1 billion, 1 US $ = JPY 110) in 2016. This accounts for 1.1% of national healthcare expenditure. On the other hand, according to a survey of the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society, in the case of the US, IT budgets of hospitals accounted for 3.2% in 2012 as a percentage of the total cost which increased from 2.5% in 2004. Therefore, if we include healthcare entities other than hospitals that have a lower IT investment burden, we can estimate that the ratio in the US is within the 2% range. The Japanese government aims to become the world's most advanced country in terms of IT utilization in healthcare. However, to achieve such a goal, Japan has to raise the proportion of IT investment in healthcare expenditure to more than 2%.
As Table 1 shows, the penetration rate of electronic medical records, which is the infrastructure for utilizing IT in healthcare, has been rising. However, with regards to information sharing among care service institutions that take on different functions, Japan is hardly advanced. For example, the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare advertises AJISAI NET (Note 1) of Nagasaki prefecture (population 1,352 thousand) as a best practice of a medical information sharing network. The utilization rate of AJISAI NET which began operating in 2004 is only 5.4% (73 thousand users) as of December 2017. The main reason is that there are an overwhelming 322 institutions that do not disclose their information but only view the electronic medical records of other institutions, compared to 34 institutions that disclose electronic medical records to others. Given this, it cannot be called a medical information sharing network.
(Note 1) AJISAI is hydrangea in English
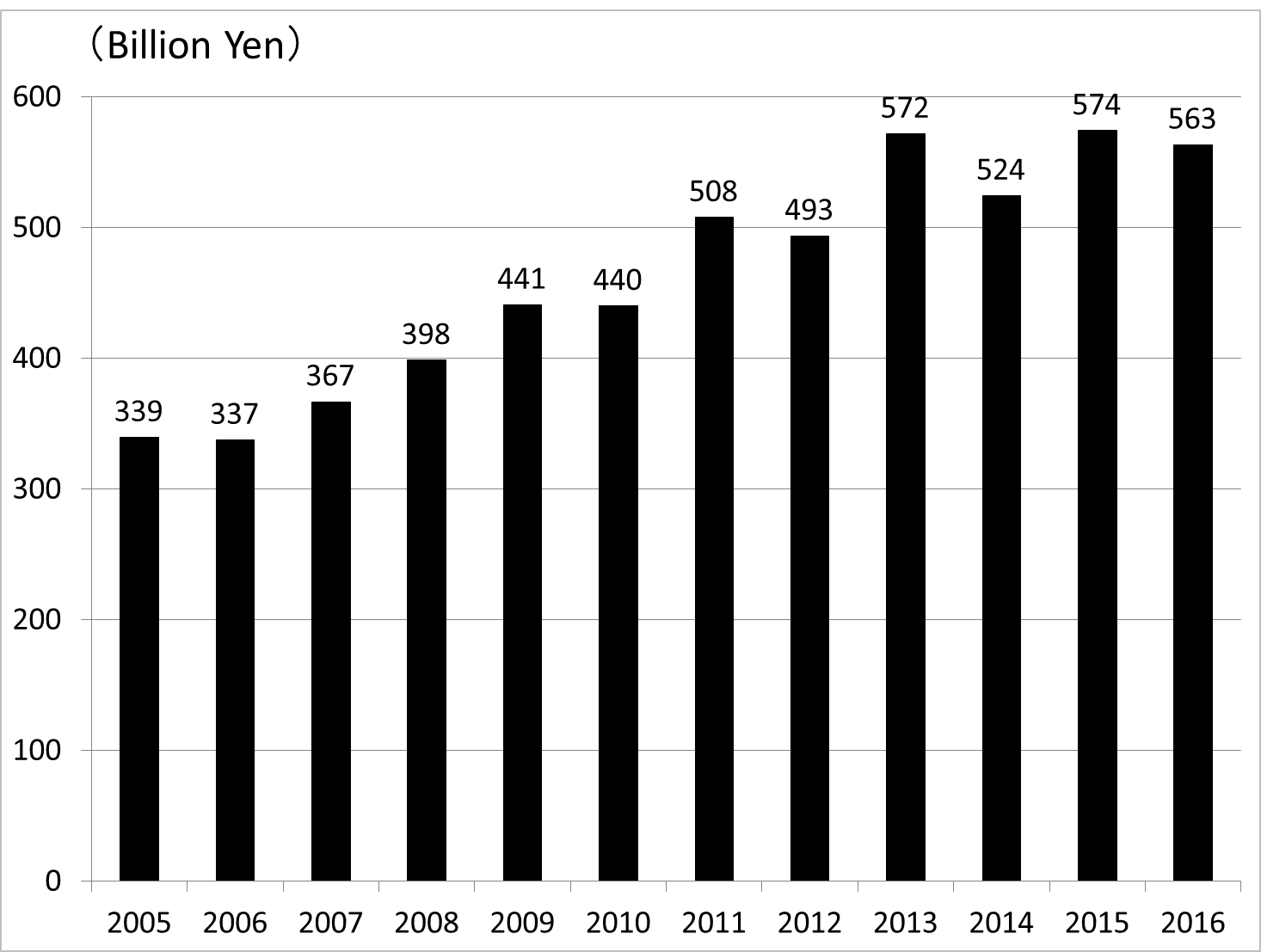
(Source)Japanese Association of Healthcare Information Systems Industry

(Source)Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare
